Beginner Bookkeeping Guide for Small Businesses
Starting your own business is exciting, but before diving in, it’s essential to understand the basics of bookkeeping. Even without prior bookkeeping knowledge, this guide will help you set up a simple system to manage your business finances with confidence.


What Is Bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping is the process of recording all financial transactions, including sales, purchases, payments, and receipts. Accurate bookkeeping enables you to track performance, manage cash flow, and prepare for tax season.
Bookkeeping vs Accounting
Bookkeeping is the process of recording all your business transactions, such as sales and expenses, to keep track of the money coming in and going out. Accounting takes it a step further by analysing this information to prepare reports, assist with tax filings, and inform business decisions.
Think of bookkeeping as keeping your financial records organised, while accounting helps you understand what those records mean for your business.
Single Entry vs. Double Entry Bookkeeping
Before choosing a bookkeeping method, it’s essential to understand the key differences between single-entry and double-entry systems. The right choice depends on the size and complexity of your business. Here’s a breakdown of each approach and how they work in practice.
Single-entry Bookkeeping is a simple method suitable for very small businesses or personal finances. It records income and expenses using a spreadsheet or ledger book.
Double-entry bookkeeping records every transaction twice — as both a debit and a credit — and provides a more comprehensive financial picture. It supports the creation of profit and loss accounts and Balance Sheets.
Accounting software makes double-entry much easier by automating entries. For example, issuing a sales invoice will automatically update both sales revenue and accounts receivable.
The Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping. It shows the relationship between what your business owns and owes:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This means everything your business owns (assets) is funded either by borrowing money (liabilities) or by your investment (equity). Keeping this equation balanced ensures your accounts are accurate and helps maintain a clear picture of your financial position.
Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
Understanding the difference between cash and accrual accounting is essential for managing your finances accurately. These two methods determine when income and expenses are recorded and can affect how your financial position is reported.
- Cash Basis records transactions when money changes hands.
- Accrual Basis records income when earned and expenses when incurred.
Small businesses can often start with the cash basis method, but growing or VAT-registered businesses may need to switch to accrual accounting.
Example: Imagine you send a £1,000 invoice to a client on 10th December for work completed in December, but they don’t pay until 5th January.
- Cash Accounting: You record the income on 5th January, when the money is received.
- Accrual Accounting: You record the income on 10th December, when the invoice was issued.
Choosing a System: Bookkeeping Software or Spreadsheets?
Choosing the best bookkeeping system depends on the size and needs of your business. For very small businesses or those just starting, a simple ledger book or Excel bookkeeping templates can be an affordable and easy way to track income and expenses.
As your business grows, using accounting software can save time, reduce errors, and provide more detailed financial reports. Understanding the pros and cons of each option will help you select the system that best suits your needs.
Ledger Books
A ledger book is a simple, manual method for recording income and expenses. It’s low-cost and easy to use for very small businesses, but can be time-consuming and less accurate. As your business grows, switching to digital tools may save time and reduce errors.
Excel Templates
Excel bookkeeping templates are a great option when you’re starting out. We offer over 25 free templates, including:
- Cash Books
- Sales Invoices
- Budget Trackers
- Accounts Receivable
- Accounts Payable
- Petty Cash
All templates are free to download, easy to use, and come with clear instructions and examples.
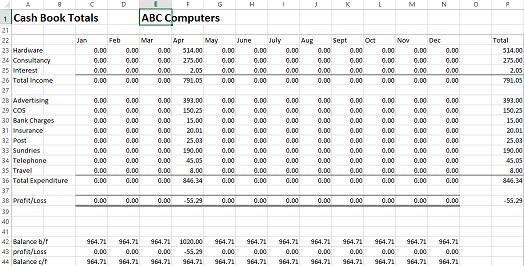
Below is an example of our simple cashbook template.

Bookkeeping Software
Beginner Bookkeeping software can automate many tasks such as invoicing, bank reconciliation, and financial reporting, saving you valuable time and reducing the chance of errors.
Popular options include QuickBooks, Xero, Sage UK, Zoho Books and Dext. Dext is especially useful for automating expense management by capturing and processing receipts and invoices digitally, making it easier to keep your records up to date.
Best Small Business


| From £16 per month |
| Free Trial |
| Integration with apps |
| 90% Discount – 4 Months |
Best Free


| From £12 per month |
| 1,000 invoices PA Free |
| Integrate with Zoho Apps |
| No Discount |
Most of these software solutions offer free trials, so you can explore their features and find the best fit for your business needs without any initial commitment.
Financial Reports
Understanding financial reports, also known as financial statements, is essential for tracking your business’s performance and making informed decisions. These reports summarise key financial data, showing how your business is doing over time and at specific points. Below are the primary types of financial reports that every business owner should be familiar with.
Profit and Loss (P&L)
The Profit and Loss report displays your business’s income and expenses over a specified period—monthly, quarterly, or yearly. It helps you understand whether your business is making a profit or loss and is key for budgeting and tax reporting.
Balance Sheet
A Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of your business’s financial position at a specific point in time. It lists assets (what you own), liabilities (what you owe), and equity (your investment in the business), helping you understand your overall financial health.


Cash Flow Report
A Cash Flow Statement shows how cash moves in and out of your business. It helps you track when money comes in and goes out, allowing you to manage your cash effectively.
Trial Balance
The Trial Balance is a report that lists all your general ledger accounts and their balances. It’s used to check that total debits equal total credits, which helps identify any errors in your bookkeeping before creating final financial statements.
Should You Hire a Bookkeeper?
If you’re confident managing your records, you may only need a professional bookkeeper or accountant for year-end submissions. But hiring a bookkeeper regularly can save time and reduce errors, especially as your business grows.
Keeping Bookkeeping Records
It’s essential to keep all source documents—such as invoices, receipts, bank statements, and bills—for at least six years, in line with HMRC requirements. A clear and consistent filing system helps you stay organised and makes it easier to find records when needed.
You can store records digitally or on paper. Digital storage is often more efficient, especially when using bookkeeping software. Many systems allow you to upload and attach invoices and bills directly to transactions, keeping everything in one place. Whether you file documents by month or by supplier/customer, choose a method that works best for your business and stick to it.
How Often Should You Do Your Books?
The size of your business will determine how often financial information is required and how frequently you perform bookkeeping. Here is a rough guide:
- Large businesses: daily to have up-to-date figures
- Small businesses: weekly or monthly
- Minimum: annually, for tax returns
Staying consistent helps you avoid falling behind.
Common Bookkeeping Terms
Understanding bookkeeping basics starts with learning the key terms you’ll encounter regularly. These terms form the foundation of your financial records, enabling you to understand reports, transactions, and account balances. Below are some of the most common bookkeeping terms every small business owner should know.
- Accounts Receivable: money owed by customers
- Accounts Payable: money owed to suppliers
- Chart of Accounts: a list of all account categories
- Double Entry: two-sided recording of transactions
- Equity: owner’s share in the business
- Basic Accounting Equation: the image below shows the basic accounting equation


Download our free list of bookkeeping terms below.
[maxbutton id=”4″ url=”https://www.businessaccountingbasics.co.uk/bookkeeping-terms/” text=”Bookkeeping Terms” ]
FAQs
Can I Do My Own Bookkeeping?
Yes, especially if your business is small. Use templates or simple software, and stay organised. If you’re unsure about how to get started, consider seeking the help of a bookkeeper or accountant.
Are There Free Bookkeeping Courses?
The Internet has many free online courses to help business owners learn bookkeeping. At Business Accounting Basics, we have a wealth of information; using the search function at the top will help you find the most relevant articles.
We have also written a post featuring the best free online courses, along with brief descriptions. It is also worth checking YouTube for video tutorials.
Should I Have Separate Bank Accounts?
Yes, having a separate business bank account helps keep your personal and business finances organised. It makes bookkeeping easier, ensures accurate records, and is required for limited companies.
Final Thoughts
Take your time choosing tools and systems that suit your business. Whether you use spreadsheets or software, the key is to stay consistent and organised. If in doubt, consult a bookkeeper — they may save you money in the long run.
For further reading, check out our bookkeeping basics page.






